Alpha Lipoic Acid
As a supplement, ALA has been used to support the treatment of various conditions such as diabetes, HIV, cancer and liver ailments.
Recently, it has garnered increased attention for its potential benefits in promoting weight loss.
Alpha lipoic acid is naturally produced by the body and can be obtained from dietary sources such as red meat, organ meat, vegetables and yeast.
Once administered, ALA injections are quickly absorbed and distributed throughout the major organs.
It plays a vital role in the conversion of glucose to energy within the mitochondria.
By mimicking insulin, ALA injections improve glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, facilitating the transportation of glucose into cells and reducing fat storage.
Additionally, ALA enhances the conversion of carbohydrates into energy, limiting their conversion into fats. These effects support weight management and optimal blood sugar levels, making ALA injections beneficial for individuals looking to improve their metabolic health.
Alpha Lipoic Acid Injections:
1. May slow memory loss
2. May fight premature skin aging from UV damage
3. Help maintain optimal blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity
4. Reduce the risk of oxidative damage and inflammation
5. Support healthy nerve function and reduce symptoms of neuropathy
6. Enhance energy production and metabolism
7. Support cardiovascular health and protect against heart-related complications
8. May boost immune system function and enhance disease resistance.
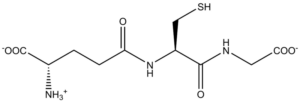
Amino Blend
Amino Blend injections can address these symptoms more effectively than pill or tablet forms.
They are found in foods such as meats, fish, and soybeans but many people also use amino acid injections and supplements to boost athletic performance or improve their mood.
Amino acids are categorized into three groups: essential, nonessential, and conditional.
Essential amino acids cannot be made within the body and must come from external sources, such as diet or supplements. Nonessential amino acids are produced within the body, and conditional amino acids are usually produced within the body.
During periods of stress, illness, or injury, the body may not be able to create enough of these, and they become essential amino acids that require external supplementation.
Our amino acid blend also provides your body with essential and non-essential amino acids to promote overall health.
Ascorbic Acid
Ascorbic acid is a powerful antioxidant, meaning it helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can lead to oxidative stress and contribute to various chronic diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and certain neurological disorders. It also plays a vital role in the synthesis of collagen, a protein found in connective tissues, skin, blood vessels and bones. Collagen is essential for wound healing, maintaining healthy skin, and supporting the structure and integrity of various body tissues.
Extremely low levels of vitamin C can cause a condition referred to as scurvy. Symptoms of scurvy include rash or brown spots on the skin, muscle weakness, pale skin, joint pain, tiredness, depression, or tooth loss.
Ascorbic acid is important as it is needed to maintain the health of skin, teeth, cartilage, bone and blood vessels.
Ascorbic acid also helps boost the activity of other antioxidants in the body, further supporting immune function.
It has been associated with several other potential health benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, age-related macular degeneration and certain types of cancer, and may also have anti-inflammatory properties that play a role in supporting brain health.
B-Complex Vitamins
Vitamin B complex is essential for a wide variety of functions in the human body, Its deficiency can also lead to several disorders including chronic neurological ones. Biochemically, different structures are grouped together under B complex on the basis of their natural occurrence in same type of food and solubility in water. Since humans are not able to synthesize vitamins in B complex on their own and these vitamins are easily excreted from the body through urine, their regular intake is essential to maintain energy production, DNA/RNA synthesis/repair, genomic and non-genomic methylation as well as synthesis of numerous neurochemicals and signalling molecules. B complex deficiency is normally caused due to four possible reasons; high consumption of processed and refined food, with lack of dairy and meat-based food in diet, excessive consumption of alcohol, impaired absorption from the gastrointestinal tract or impaired storage and use by liver
B vitamins play different roles but their functions are inter-related and complementary. They work as coenzyme in several biochemical reactions to activate enzyme reaction of corresponding protein by creating holoenzyme. As holoenzyme they participate in the majority of cellular processes.
Although vitamin B1 and B6 participate more actively in the methionine cycle and citric acid cycle, which is the mitochondrial energy production process,1 the entire vitamin B group is involved in its successful execution. B vitamins also help to maintain the health of nervous system by playing a crucial role in the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system functions.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) serves as a coenzyme with transketolase enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway of glycolysis. This pathway generates pentose sugar for synthesis of amino acid and nucleic acid and converts glucose to ribulose-5-phosphate via retrieving the carbon from the pentose phosphate shunt. Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) plays an important role in many biologically important redox reactions such as energy producing, biosynthetic, detoxifying and electron scavenging pathways910 as a precursor of coenzyme flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Riboflavin is also essential for the metabolism of homocysteine, as a cofactor for methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and methionine synthase reductase (MTRR).
In the citric acid cycle, Vitamin B3 (Niacin) is involved in the formation of acetyl-CoA while conversion of its co-enzyme takes places from NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to NADH. In the anabolic methionine cycle, niacin, in the form of NAD, is a necessary co-factor for the enzymes dihydrofolate reductase in the folate/tetrahydrobiopterin cycle and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase.1 Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) is a component of coenzyme A. At least 70 enzymes utilize coenzyme A for the metabolism of fat, protein, carbohydrates and proper functioning of citric acid cycle. It is also involved in synthesis of several neural transmitters.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) acts as a necessary cofactor in the folate cycle and combines with serine hydroxymethyl transferase to effect the conversion of tetrahydrofolate(THF) to 5,10 methylene THF. B6 is a rate limiting cofactor in the synthesis of several neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), noradrenaline and the hormone melatonin.1 Even a minor deficiency of B6 can cause a substantial down-regulation of these neurotransmitters. B6 also plays an important role in immune functions and is also a bio-marker of inflammation with its down-regulation being associated with severe inflammation.
Vitamin B7 (Biotin) is a water-soluble vitamin that can be found in various foods like eggs, milk and bananas. It plays a crucial role in cell growth, carbohydrate metabolism and fatty acid synthesis, playing a key role in supporting overall health. Biotin is involved in metabolic processes related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids, while also influencing cell growth and blood sugar levels. People often take biotin supplements for hair loss, brittle nails, and nerve damage. Additionally, biotin is believed to have anti-inflammatory effects, improve cognitive function, raise HDL (good) cholesterol and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.
Vitamin B12, a vitamin found in food and used as a dietary supplement. Vitamin B12 helps to utilize fats and carbohydrates for energy and make new proteins. It is important in the maintenance of our metabolism, blood cells, and nerve function. Most people get enough vitamin B12 in their diet, but some need supplementation. Certain health conditions such as intestinal or stomach problems, poor nutrition, cancer, HIV, pregnancy, old age, veganism and alcoholism can cause vitamin B12 deficiency. Low levels of vitamin B12 can lead to fatigue and anemia in milder cases. More serious deficiencies have the potential to impair heart and neurological function, leading to a wide range of serious symptoms, including but not limited to tinnitus, severe joint pain, memory problems, depression, anxiety, poor muscle function, ataxia and changes in reflexes. Infertility can also occur in individuals with insufficient B12. Early intervention and treatment of deficiencies are key to maintaining healthy bodily function.U & B:
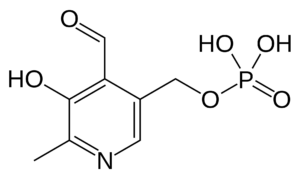
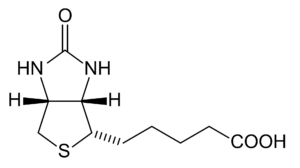
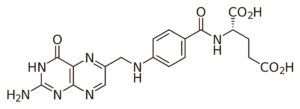
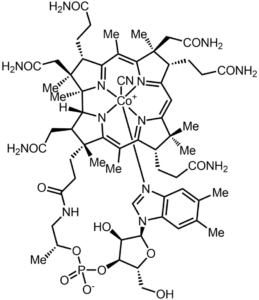
Biotin
Biotin is involved in metabolic processes related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids, while also influencing cell growth and blood sugar levels.
Biotin is often taken for hair loss, brittle nails, and nerve damage. Additionally, biotin is believed to have anti-inflammatory effects, improve cognitive function, raise HDL (good) cholesterol and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.
What is Biotin Deficiency?
Biotin deficiency is rare but can cause issues such as hair loss, skin problems, and neurological symptoms. Although it’s uncommon to have low biotin levels since only a small amount is needed for proper function, it is still possible. Unlike other vitamin deficiencies, there isn’t a reliable lab test for detecting low biotin levels, so it’s best identified through symptoms. These symptoms may include thinning hair, red/scaly rash around the nose, eyes, and mouth, depression, fatigue, hallucinations and tingling sensations in the arms and legs.While oral biotin supplements are commonly used to promote hair growth and strengthen nails, injections are more effective when immediate results are desired.
Injections allow for maximum absorption of the vitamin directly into the body, bypassing the digestive system’s metabolic processes that can affect the bioavailability of oral supplements.

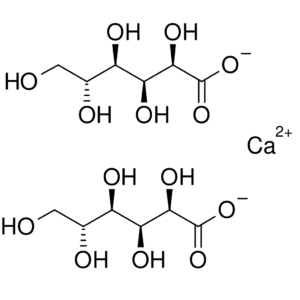
Calcium Chloride / Gluconate
Calcium chloride is used in the treatment of hypocalcemia (low calcium), hyperkalemia (high potassium), and hypermagnesemia (high magnesium).
Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the body, and it is the major component of your bones.
Calcium is essential to the function of our nervous and muscular systems, the coagulation of blood, and for normal contractility of the heart.
Calcium also affects the secretory activity of endocrine and exocrine glands.
In addition, it plays a crucial role in intracellular signaling, neurotransmitter release and maintaining cell membrane potential. In water, calcium chloride breaks down into calcium and chloride ions. These ions are regular components of body fluids and depend on other physiological mechanisms to maintain the balance between one’s intake and output.
Approximately 80% of body calcium gets excreted in the feces as insoluble salts, and the remaining 20% is excreted through the urine.
What Is Calcium Chloride Prescribed For?
Calcium chloride injections may be used in the treatment of hypocalcemia (low calcium), hyperkalemia (high potassium) and hypermagnesemia (high magnesium). It is also used in the immediate treatment of hypocalcemic tetany, which causes muscle spasms due to abnormally low levels of calcium in the body.Additionally, calcium chloride is used as an additive in cardiac resuscitation, helping to stabilize the heart during instances of arrhythmias or cardiac arrest. It is sometimes administered in critical situations to improve the contractility of the heart. In some cases, calcium chloride is also utilized in the management of calcium channel blocker toxicity.
Calcium chloride also helps to maintain bone health and prevent muscle spasms.
Moreover, by helping to correct imbalances of calcium and other minerals, calcium chloride can be essential in treating certain life-threatening conditions. It is also beneficial in promoting the normal function of enzymes and hormones.
Hydroxo B12
As a supplement, ALA has been used to support the treatment of various conditions such as diabetes, HIV, cancer and liver ailments.
Recently, it has garnered increased attention for its potential benefits in promoting weight loss.
Vitamin B12 helps to utilize fats and carbohydrates for energy and make new proteins. It is important in the maintenance of our metabolism, blood cells, and nerve function.
Most people get enough vitamin B12 in their diet, but some need supplementation. Certain health conditions such as intestinal or stomach problems, poor nutrition, cancer, HIV, pregnancy, old age, veganism and alcoholism can cause vitamin B12 deficiency.
Low levels of vitamin B12 can lead to fatigue and anemia in milder cases. More serious deficiencies have the potential to impair heart and neurological function, leading to a wide range of serious symptoms, including but not limited to tinnitus, severe joint pain, memory problems, depression, anxiety, poor muscle function, ataxia and changes in reflexes. Infertility can also occur in individuals with insufficient B12.
Early intervention and treatment of deficiencies are key to maintaining healthy bodily function.
Vitamin B12 helps the body convert fat and carbohydrates to energy and may be beneficial as part of a weight loss program.

L-Carnitine
As an injectable supplement, L-carnitine has been employed to support various health conditions, including heart and circulatory issues, as well as to enhance athletic performance.
Recently, it has gained prominence for its potential benefits in promoting weight loss and improving overall well-being.
Carnitine also transports toxic compounds out of the cellular organelles, preventing any accumulation.
Given these functions, carnitine is concentrated in tissues that utilize fatty acids as fuel, like skeletal and cardiac muscles.
For most people, the body makes enough carnitine. However, some people have genetic or medical conditions that prevent their bodies from meeting the necessary amount. This is when oral or injected supplementation is essential.
What Is ‘L’ (vs ‘D’) Levocarnitine?
Carnitine occurs in two main forms: D-carnitine and L-carnitine. They are isomers (or mirror images) of each other. L-carnitine, or levocarnitine, is the active form found in the body that transports fat to cells to be used as fuel in metabolic processes. D-carnitine does not occur naturally in humans. L-carnitine is synthesized in the brain, liver, and kidneys from the amino acids methionine and lysine and is critical to heart and brain function, muscle movement, and several other body processes.Insufficient carnitine can lead to problems in the liver, heart, and muscles.
What Is Carnitine Prescribed For?
Carnitine is indicated in those with cardiovascular disease, renal (kidney) insufficiency, male infertility, diabetes, muscular disease, and HIV/AIDS.L-Carnitine may help reduce muscle damage during resistance training.
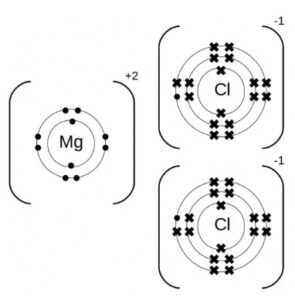
Magnesium Chloride
It is essential for nerve function, cellular metabolism, muscle contraction, and the maintenance of heart rhythm. Magnesium also facilitates the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy molecule in cells, and is involved in the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
Furthermore, magnesium contributes to the structural development of bones and is required for the proper function of various enzymes. Although most individuals acquire sufficient magnesium through a balanced diet, certain circumstances may warrant supplementation. Foods rich in magnesium typically contain fiber and include nuts (such as almonds and cashews), seeds (like pumpkin seeds), legumes, leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), whole grains, and fortified cereals. Moreover, certain fruits such as avocados and bananas, as well as dark chocolate and fatty fish, are good sources of magnesium.
Magnesium chloride is one of the various forms of magnesium salts and is often chosen for medical use due to its high bioavailability.
Individuals more prone to magnesium deficiency include women (especially during pregnancy), African Americans, the elderly, and those with gastrointestinal disorders that affect nutrient absorption.
Chronic magnesium deficiency is associated with numerous health conditions, such as osteoporosis, high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), diabetes, and stroke. Additional factors that can contribute to magnesium deficiency include alcoholism, poor diet, chronic stress, certain medications (like diuretics), and poorly controlled diabetes.
What Is Magnesium Chloride Prescribed For?
Magnesium chloride can be prescribed for a variety of health conditions and for preventive health measures. Among its uses is addressing magnesium deficiency by restoring normal magnesium levels in individuals who might be deficient due to inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption or excessive loss.It can also be of benefit in diabetes management, as supplementing with magnesium chloride may improve insulin sensitivity and glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
For heart health, magnesium chloride can help regulate heart rhythms and may play a role in reducing the risk of heart disease. High blood pressure is another area where magnesium supplementation can be beneficial by contributing to lowering blood pressure levels.
In the case of osteoporosis, magnesium is vital for bone health and can be instrumental in preventing bone loss.
Furthermore, individuals with migraines sometimes have low levels of magnesium, and supplementation with magnesium chloride can reduce the frequency of migraines.
As an osmotic laxative, magnesium chloride is also effective in relieving constipation.
It plays a role in reducing stress and anxiety by regulating neurotransmitters.
Another significant benefit of magnesium chloride is the improvement of sleep quality; by calming the nervous system and maintaining healthy levels of the neurotransmitter GABA, it promotes sleep.
Additionally, it aids in the relaxation of muscle fibers, which in turn can lead to a reduction in cramps and muscle tension.
Magnesium is also essential for calcium absorption and plays a critical role in the formation and maintenance of healthy bones, thereby contributing to bone health.
L-Glutamine
Glutamine is a vital amino acid that serves as a building block for proteins in the body. While the body can usually synthesize enough glutamine, during times of stress or trauma, additional supplementation may be necessary.
Glutamine provides the necessary nitrogen and carbon for various cellular processes, including the production of amino acids and glucose. Consequently, glutamine plays a vital role in fueling the body’s natural healing processes and promoting healthy organ function.
While the body can usually synthesize enough glutamine, in times of stress like traumatic injury or illness, the demand for glutamine exceeds what the muscles can produce. In such cases, additional glutamine can be obtained from the diet, found in protein-rich sources like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices, wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso.
What Is Glutamine Prescribed For?
Glutamine is commonly prescribed to alleviate side effects of chemotherapy, such as diarrhea, mouth pain/swelling, neuropathy, and muscle/joint pain. It is also used for digestive conditions like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and ulcers.Furthermore, glutamine is employed to enhance exercise performance, manage sickle cell anemia, and support alcohol withdrawal.
They may help muscles recover faster after intense workouts and reduce the recovery time for wounds and burns. L-glutamine has also demonstrated potential for improving symptoms of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), leaky gut and ulcers.
Additionally, as a precursor to glutamate, glutamine could have positive effects on brain-related issues such as Reye’s Syndrome, epilepsy, anxiety, depression and addiction.
Additionally, some studies suggest that l-glutamine may aid in weight loss by supporting metabolism and reducing muscle wasting.
L-Glutathione
Glutathione has many functions.
It is vital to mitochondrial function and necessary to produce DNA.
Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier means it plays an important role in removing toxins, such as mercury, from the brain and other cells.
It is key in supporting immune function, metabolism, forming sperm cells, tissue building and repair, and helping with certain enzyme functions.
As a powerful antioxidant, it may help fight the effects of free radicals, which cause oxidative stress, damage healthy cells, and contribute to aging and certain degenerative illnesses. Unlike most antioxidants, glutathione can be made in the human liver.
Glutathione can be found in every cell of the human body.
L-Glutathione is found in many foods, including spinach and avocados, but is poorly absorbed by the body when consumed orally. Supplements that can support glutathione production include curcumin, N-acetylcysteine, selenium, silymarin, vitamin C, and Vitamin E.
Glutathione levels in the body naturally decline as we age but can also be reduced by factors like stress, malnutrition, and environmental toxins.
Glutathione is an antioxidant and is beneficial for many disease states as well as helping people live a healthier life. It may improve immune response, help to metabolize toxins and activate enzymes, aid the liver in metabolizing alcohol, reduce the amount of fat stored in the belly, help to reduce oxidative stress and improve complexion.
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)
Examples of some processes that are dependent on NAD are glycolysis (the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate and hydrogen), citric acid or tricarboxylic acid cycle (the release of stored energy from carbohydrates, proteins and fats through the oxidation of acetyl CoA), the oxidation or breakdown of fatty acids, DNA repair, inflammatory responses, among many other processes.
NAD usually undergoes either oxidation or reduction as it exerts its effects on the body’s metabolic processes; the oxidized variant of NAD is referred to as NAD+.
Importance of NAD+ In the Human Body
As stated earlier, NAD+ is crucial for a number of key physiological processes within the human body. A deficiency in NAD+, or a disruption in NAD+ homeostasis in the body, may impair these physiologic processes, which may result in different illnesses or disease conditions. Discussed below are some of the many physiologic processes that are dependent on NAD+.1) Genomic Stability
On a daily basis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are released endogenously within the body; these substances cause damage to cellular DNA. In addition, exogenous factors such as carcinogens, chemical mutagens, as well as radiation may also result in cellular DNA damage. When cellular DNA damage occurs due to either endogenous or exogenous factors, genomic instability occurs, which may result in cancer development and an increased rate of cellular aging.In order to minimize cellular DNA damage and its consequences, there is a process in the body known as DNA-damage response (DDR). DDR is a process that detects and repairs any damaged DNA in the body. DDR is a process that is highly dependent on NAD+; when amounts of NAD+ are low in the body, the DDR process is impaired, resulting in increased damage to the cellular DNA.
2) Genetic Expression
The means by which genetic information in cellular DNA is used to produce the relevant proteins or substances in the human body is known as genetic expression. Genetic expression is the process that is responsible for the development of all the physical features that define an individual, such as hair and skin color, among other physical characteristics.One of the mechanisms by which genetic expression successfully occurs in the body is through modifying a product known as histones. Histone modification is a NAD+ dependent process; a deficiency in NAD+ levels may disrupt histone modification, which may impair genetic expression. NAD+ deficiency may also result in the methylation of cellular DNA so that genes are not expressed appropriately; this is known as genetic silencing.
3) Immunity and Inflammation
Studies have shown that NAD+ levels in the human body determine the extent as well as the effectiveness of immune responses during infection. Increased levels of NAD+ during an infection increase oxidative phosphorylation in macrophages, which makes them better able to neutralize the organism causing the infection.In addition to the increased expression of macrophages, NAD+ also exerts anti-inflammatory effects during an infectious process. Studies have shown that the expression of inflammatory markers such as Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-a) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) significantly diminish when there are high cellular levels of NAD+ and its precursors.
4) Energy Metabolism
Several metabolic pathways in the human body result in the release of energy. Some examples of the energy metabolic pathways are glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid oxidation, and ethanol metabolism. All the energy metabolic pathways require the presence of NAD+ as a coenzyme to function properly. In the glycolytic pathway, NAD+ facilitates the catalytic reactions of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GADPH) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). In the Krebs cycle, NAD+ functions as a coenzyme for the rate-limiting enzymes alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and malate dehydrogenase. Alcohol metabolism, which occurs in liver cells, also requires NAD+ as a cofactor for the process’s successful execution. A deficiency of NAD+ in the body may impact all these processes and negatively impact the effectiveness by which energy is generated and utilized by the body.5) Circadian Clock
The circadian clock, also known as the biological clock or circadian rhythm, is an internal endogenous process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle in the human body. This internal clock helps the body adjust to different times of the day or the different seasons. The accuracy and effectiveness of the circadian clock are due in part to cellular levels of NAD+. A deficiency of NAD+ may disrupt the circadian rhythm and result in effects such as daytime sleepiness, restless sleep, hormonal imbalances, and mood alterations, among others.6) Cardiovascular Function
The heart is the most metabolically active organ in the human body because it is constantly beating. Studies have shown that normal NAD+ levels are essential in maintaining the metabolic activity of the heart. Furthermore, in the event of a significant cardiac event such as a transient ischemic attack or myocardial infarction, normal levels of NAD+ help in the recovery from injury. Other studies have shown that a deficiency in NAD+ may result in cardiac disorders such as cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis.7) Kidney Function
Generally, renal function has a tendency to decrease as people get older. It is suspected that reduced levels of NAD+ in the elderly may have a role to play in the reduction in renal function. Research has indicated increased protection against acute renal injury when individuals were given NAD+ supplements. In addition, NAD+ supplements stimulated the release of prostaglandin E2, which serves to improve renal function after an acute renal injury.8) Liver Function
Normal NAD+ levels in the body are essential for the optimal functioning of the liver. Specific enzymes in the NAD+ pathways protect the liver from conditions such as hepatic fibrosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Several studies have been performed that show that giving individuals NAD+ supplements may boost the liver’s overall health, protect it from toxic illnesses, and enhance its capacity for regeneration after a hepatic injury.9) Neurological Function
NAD+ and its precursors have been shown to have a protective effect on the neurons in the brain after a significant neurological event such as a stroke. Having normal levels of NAD+ in the body is essential to the normal functioning and survival of cerebral neurons. Additionally, NAD+ supplements have shown some benefits in treating and preventing some neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease; this is not definite, however, and there are several ongoing studies still exploring this possibility.1) Addiction Therapy
One of the most common reasons why IV NAD+ therapy may be considered in some individuals is in the management of addiction. IV NAD+ may benefit patients weaning off opioid, alcohol, chemical, or prescription drug dependencies; it may also serve to minimize the severity of withdrawal symptoms. While the mechanism of how NAD+ works in this regard is still under investigation, it is believed that IV NAD+ helps flush drugs out of the body and reduce cravings.2) Improved Cognition
As has previously been stated, NAD+ has been shown to exert both protective and stimulatory effects on the brain. For this reason, IV NAD+ therapy may be administered to potentially enhance memory, improve concentration, improve the ability to focus, enhance brain regeneration, and improve overall neurological function. Studies are still ongoing regarding the precise means by which exogenous NAD+ supplementation exerts these effects.3) Chronic Fatigue
IV NAD+ therapy has been used in the management of individuals with chronic fatigue and low energy levels. NAD+ is an essential cofactor in the glycolytic pathway and tricarboxylic acid pathways; these pathways result in Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) production, which is the energy source of the human body. Through exogenous NAD+ supplementation, ATP levels in the body are increased which may have a resulting effect in boosting energy levels and reducing feelings of fatigue.4) Athletic Performance
Due to its role in ATP production, some athletes have used IV NAD+ therapy to enhance their athletic capabilities and performance. IV NAD+ supplements may boost energy levels, improve cognition, and increase reaction times in athletes during competitions or other athletic events. In addition, studies have shown that NAD+ supplementation may assist in muscle development as well as muscle repair, leading to muscle hypertrophy and muscle hyperplasia.5) Pain Management
One of the more novel reasons why some individuals receive IV NAD+ therapy is in managing pain. NAD+ is known to exert significant anti-inflammatory actions within body and may be used to reduce the inflammation that typically occurs with pain and, thereby, offer some relief from pain. Studies into the use of supplemental NAD+ as a form of pain control are still ongoing and the results so far are not yet definitive.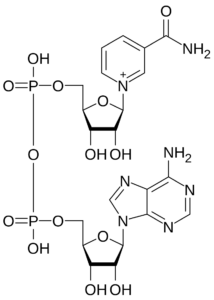
Odansetron
Pregnancy
Ondansetron is used off-label to treat morning sickness and hyperemesis gravidarum of pregnancy. It is typically used after other antinausea drugs have failed.
There appears to be a low risk of harm to the baby with use during pregnancy, though there may be an increase in heart problems among the babies.
Cyclic vomiting syndrome
Ondansetron is one of several antiemetic drugs used during the vomiting phase of cyclic vomiting syndrome.
Gastroenteritis
Trials in emergency department settings support the use of ondansetron to reduce vomiting associated with gastroenteritis and dehydration. A retrospective review found it was used commonly for this purpose, being administered in over 58% of cases.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
In one study of patients with IBS-D variant ondansetron showed statistically significant effect on stool consistency and bloating.
Pyridoxine HCL
Pyridoxine hydrochloride, commonly recognized as vitamin B6, is an essential nutrient vital for maintaining our overall health. This crucial vitamin participates in an array of bodily functions, including promoting the health of our nerves, skin, and red blood cells.
Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Neurotransmitters, chemicals vital for brain function and mental health, rely on PLP for their synthesis. Vitamin B6 is involved in the production of serotonin, dopamine and GABA – crucial neurotransmitters that regulate mood, sleep, and other functions.
Hemoglobin Production: Hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in our red blood cells, needs vitamin B6 for its production. This function is critical for delivering oxygen throughout the body.
Anti-inflammatory and Immune Function: Vitamin B6 is known to aid in reducing inflammation and boosting the immune system. It facilitates the production of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell involved in immune responses.
People with health conditions like kidney disease, autoimmune disorders or malabsorption syndromes, which can impede vitamin B6 absorption, may need supplemental B6.
Certain medications, including specific antiepileptics and tuberculosis drugs, can interfere with vitamin B6 metabolism, potentially causing a deficiency.
Additionally, the elderly population may have decreased absorption or utilization of dietary vitamin B6, making supplementation a viable option.
Because vitamin B6 plays a key role in the production of hemoglobin, it may be prescribed to prevent and treat certain cases of anemia.
Moreover, increased vitamin B6 levels are required during pregnancy and breastfeeding to support the developing baby’s brain and nervous system. Supplemental pyridoxine injections might be advised in these cases.

Taurine
Taurine injections may be valuable in the treatment of a variety of health concerns, including congestive heart failure, high blood pressure, hepatitis, high cholesterol, and cystic fibrosis.
Unlike most amino acids, taurine does not directly participate in protein synthesis. Instead, it is crucial in the regulation of intracellular water balance and distribution of key minerals and electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium. This activity is essential for the proper functioning of the digestive, nervous, and immune systems.
Furthermore, taurine serves as an antioxidant, fighting harmful oxidative stress that can damage cells.
Taurine has been found useful in the management of numerous health conditions like congestive heart failure, high blood pressure, hepatitis and high cholesterol.
Taurine’s antioxidant properties have also been tapped into for the mitigation of cell-damaging side effects linked with chemotherapy in cancer treatment.
What Is Taurine Prescribed For?
Taurine is used as a common ingredient in a variety of therapeutic interventions due to its broad spectrum of physiological benefits. Doctors and healthcare professionals may prescribe taurine to manage conditions such as congestive heart failure by helping the heart pump blood more effectively.Taurine can also be beneficial for controlling high blood pressure and reducing cholesterol levels, therefore contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
In the context of liver health, taurine has shown potential in alleviating symptoms of hepatitis.
Its role in energy metabolism can combat fatigue and improve exercise performance by enhancing muscle function and reducing muscle damage during workouts.
Taurine’s antioxidant properties can reduce oxidative stress, potentially slowing the aging process and protecting against various diseases.
Furthermore, taurine has been linked to improved mental performance. It is thought to have neuroprotective effects, possibly aiding in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
Some early evidence suggests taurine can help alleviate symptoms of insomnia and psychosis by regulating neurotransmitter activity in the brain.
It also has a potential role in treating certain types of anemia, where it can assist in the production and function of healthy red blood cells. However, more research is needed to fully understand and substantiate these benefits.